要想搞清楚finalize的具体机制,我们得从最简单的开始,WeakReference是java.lang.ref这个package中最简单的一个示例了,说它简单,是因为它的例子相对更明确一点,其他的例子都有各种随机性。但是,WeakReference和其他的Reference一样,在GC内部的处理流程是十分相似的。
先看例子:
public static void main(String args[]){
WeakReference
if (wo.get() != null) {
System.out.println("not null before gc");
}
System.gc();
if (wo.get() != null) {
System.out.println("not null after gc");
}
else {
System.out.println("null after gc");
}
}
这个例子的打印结果是:
not null before gc
null after gc
可以看到,在我们调用了System.gc以后,WeakReference所引用的那个对象已经没有了,这个引用变成了一个空引用了。
Reference的定义
那我们通过源码来看一下,WeakReference到底是怎么实现的:
public class WeakReference
public WeakReference(T referent) {
super(referent);
}
public WeakReference(T referent, ReferenceQueueq) {
super(referent, q);
}
}
嗯,几乎就是个空的,它的所有逻辑都在它的父类里,好,我们去看它的父类:
public abstract class Reference
private T referent; /* Treated specially by GC */
volatile ReferenceQueuequeue;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Reference next;
transient private Reference
static private class Lock { }
private static Lock lock = new Lock();
private static Reference
private static class ReferenceHandler extends Thread {
private static void ensureClassInitialized(Classclazz) {
try {
Class.forName(clazz.getName(), true, clazz.getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw (Error) new NoClassDefFoundError(e.getMessage()).initCause(e);
}
}
static {
// pre-load and initialize InterruptedException and Cleaner classes
// so that we don't get into trouble later in the run loop if there's
// memory shortage while loading/initializing them lazily.
ensureClassInitialized(InterruptedException.class);
ensureClassInitialized(Cleaner.class);
}
ReferenceHandler(ThreadGroup g, String name) {
super(g, name);
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
tryHandlePending(true);
}
}
}
static boolean tryHandlePending(boolean waitForNotify) {
Reference
Cleaner c;
try {
synchronized (lock) {
if (pending != null) {
r = pending;
c = r instanceof Cleaner ? (Cleaner) r : null;
pending = r.discovered;
r.discovered = null;
} else {
// The waiting on the lock may cause an OutOfMemoryError
// because it may try to allocate exception objects.
if (waitForNotify) {
lock.wait();
}
// retry if waited
return waitForNotify;
}
}
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {
Thread.yield();
return true;
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
return true;
}
if (c != null) {
c.clean();
return true;
}
ReferenceQueueq = r.queue;
if (q != ReferenceQueue.NULL) q.enqueue(r);
return true;
}
static {
ThreadGroup tg = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
for (ThreadGroup tgn = tg;
tgn != null;
tg = tgn, tgn = tg.getParent());
Thread handler = new ReferenceHandler(tg, "Reference Handler");
handler.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
handler.setDaemon(true);
handler.start();
SharedSecrets.setJavaLangRefAccess(new JavaLangRefAccess() {
@Override
public boolean tryHandlePendingReference() {
return tryHandlePending(false);
}
});
}
public T get() {
return this.referent;
}
public void clear() {
this.referent = null;
}
public boolean isEnqueued() {
return (this.queue == ReferenceQueue.ENQUEUED);
}
public boolean enqueue() {
return this.queue.enqueue(this);
}
Reference(T referent) {
this(referent, null);
}
Reference(T referent, ReferenceQueuequeue) {
this.referent = referent;
this.queue = (queue == null) ? ReferenceQueue.NULL : queue;
}
}
我把注释都删掉了,反正留着大家也看不懂。真的,这里面的注释对于绝大多数人一点用也没有。我会在后面随着讲解一点一点地把注释贴出来。
看上去很多,我们来拆解一下。首先,Reference有4个成员变量:referent, queue, next, discovered。我把它们标黑了,这4个成员变量是绝对绝对不能改变他们的顺序的,如果它们的顺序发生变化了,你得在Hotspot的一个很偏僻的角落里把那个逻辑也改了,才能正确工作。这个偏僻的角落十分鸡贼,我最早研究这部分的代码的时候就被绕进去过。
接下来,是三个static变量,这三个变量我们先不去管它。
再接下来是一个线程类ReferenceHandler,这个线程类在我们的例子中,还不会使用,我们暂且跳过去。
再接下来,就是get, clear以及两个构造函数。都很简单。至于ReferenceQueue这个结构,现在也不用管它。
HotSpot 中的实现
在Universe的初始化阶段,调用了这么一个神奇的函数,也就是我上文所说的特别鸡贼的地方:
void InstanceRefKlass::update_nonstatic_oop_maps(Klass* k) {
// Clear the nonstatic oop-map entries corresponding to referent
// and nextPending field. They are treated specially by the
// garbage collector.
// The discovered field is used only by the garbage collector
// and is also treated specially.
InstanceKlass* ik = InstanceKlass::cast(k);
// Check that we have the right class
debug_only(static bool first_time = true);
assert(k == SystemDictionary::Reference_klass() && first_time,
"Invalid update of maps");
debug_only(first_time = false);
assert(ik->nonstatic_oop_map_count() == 1, "just checking");
OopMapBlock* map = ik->start_of_nonstatic_oop_maps();
// Check that the current map is (2,4) - currently points at field with
// offset 2 (words) and has 4 map entries.
debug_only(int offset = java_lang_ref_Reference::referent_offset);
debug_only(unsigned int count = ((java_lang_ref_Reference::discovered_offset -
java_lang_ref_Reference::referent_offset)/heapOopSize) + 1);
if (UseSharedSpaces) {
assert(map->offset() == java_lang_ref_Reference::queue_offset &&
map->count() == 1, "just checking");
} else {
assert(map->offset() == offset && map->count() == count,
"just checking");
// Update map to (3,1) - point to offset of 3 (words) with 1 map entry.
// 下面的两行是最重要的地方。
map->set_offset(java_lang_ref_Reference::queue_offset);
map->set_count(1);
}
}
我们之前讲过Klass的作用,以及如何使用OopMapBlock对一个类的所有引用进行遍历。这个函数的目的就是修改Reference的Klass的OopMapBlock。正常情况下,我前面介绍了,Reference会有4个成员变量,那么Reference的对象布局就应该是这样:
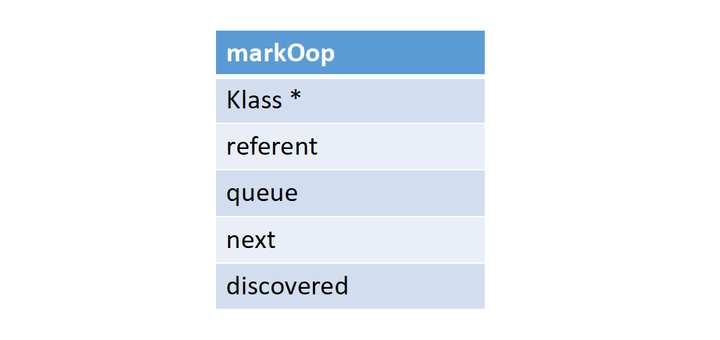
原来的OopMapBlock是(2,4),意味着从偏移为2的地方开始,一共有4个 field。修改过以后,就变成了(3,1),代表从偏移为3的地方开始,一共只有一个 filed。这样做的效果是什么呢?主要就是除了queue以外,其他的 field 在遍历的时候就都不会再去扫描了。
我们以上节课分析的 parallel gc 为例,我们知道遍历一个Klass的操作是从这里发起的:
inline void oopDesc::push_contents(PSPromotionManager* pm) {
// 每一个Java Class在JVM内部都会对应一个Klass结构。每一个Klass中都记录
// 了每个类有多少具体的域,这样我们就能通过这个Klass来计算每个实例的大小
// 以及遍历这个对象所引用的其他对象。
Klass* k = klass();
if (!k->oop_is_typeArray()) {
// It might contain oops beyond the header, so take the virtual call.
k->oop_push_contents(pm, this);
}
// Else skip it. The TypeArrayKlass in the header never needs scavenging.
}
这里, oop_push_contents是一个虚函数,对于Refence这种类型,它们的klass都是InstanceRefKlass。










